Introduction
When I was younger, I saw an advert about a Bingo club. The advert featured mostly elderly people enjoying a game of Bingo. Since then, when I heard the term “Bingo,” I pictured only elderly people playing the game. Now, I enjoy the odd game of Bingo, and I am not old, so it’s amazing what a small memory can do.
Anyway, today you will learn how to create a Bingo game in .NET. I hope you have fun.
Bingo
Bingo is a game of probability. In Bingo, players mark off numbers on cards as the numbers are drawn randomly by a caller. The winner is the first person to mark off all his or her numbers. Bingo can be played with 90 balls or 75 balls, depending on where you are.
Practical
You will use either C# or Visual Basic.NET to create a Bingo card, then pick the random numbers. Open Visual Studio and create a Windows Forms application in your language of choice. Once the default form is displayed, add the following objects onto it:
- 2 x Labels
- 2 x Buttons
- 1 x TableLayoutPanel
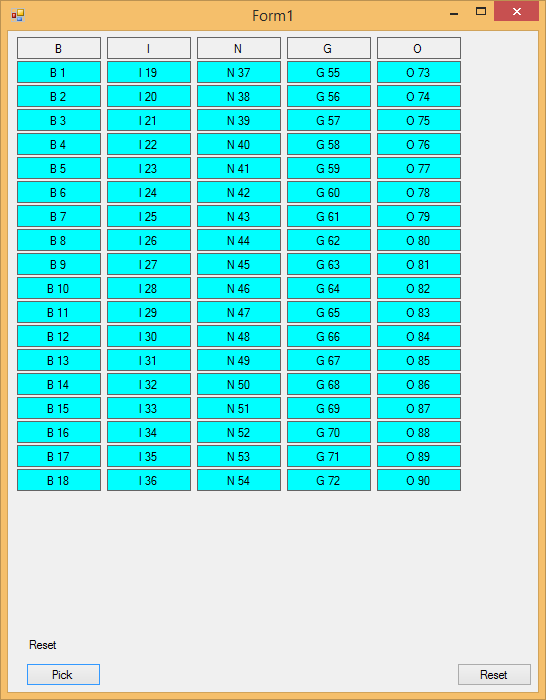
You may name these objects anything you like, although my names may be different than yours. Resize your Form’s Height. An example screen is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Design
Add the following fields and enumerations to your class.
C#
private int intRows = 18;
private char[] chrHeader = new char[] { 'B', 'I', 'N', 'G',
'O' };
private int intMinHeight = 470;
private int intMinWidth = 450;
int intWidth = 0;
int intHeight = 0;
private int intTotalCells = 0;
private int intCalledNumbers;
private Dictionary<string, Label> dicCards = new
Dictionary<string, Label>();
private Random rndRand = new Random();
enum ActiveState
{
Active = -16744448, // Green//
InActive = -16711681 // Cyan//
}
VB.NET
Private intRows As Integer = 18
Private chrHeader() As Char = New Char() {"B"c, "I"c, "N"c, _
"G"c, "O"c}
Private intMinHeight As Integer = 470
Private intMinWidth As Integer = 450
Private intTotalCells As Integer = intRows * chrHeader.Length
Private intCalledNumbers As Integer
Private dicCards As New Dictionary(Of String, Label)
Dim rndRand As New Random
Enum ActiveState
Active = -16744448 'Green'
InActive = -16711681 'Cyan'
End Enum
The Rows and Columns are created. The Height and Width of the gaming board is instantiated, and a dictionary object is created to store the cards. The ActiveState enumeration displays green or cyan, depending on whether the number has been called.
Add the following Function.
C#
public Label lblLabel()
{
intWidth = (tblBingo.Width / chrHeader.Length) - 2;
intHeight = (tblBingo.Height / (intRows + 1)) - 2;
Label lbl = new Label();
lbl.AutoSize = false;
lbl.Width = intWidth;
lbl.Height = intHeight;
lbl.TextAlign = ContentAlignment.MiddleCenter;
lbl.BorderStyle = BorderStyle.FixedSingle;
lbl.Tag = ActiveState.InActive;
return lbl;
}
VB.NET
Public Function lblLabel() As Label
Static intWidth As Integer = _
(tblBingo.Width \ chrHeader.Length) - 2
Static intHeight As Integer = _
(tblBingo.Height \ (intRows + 1)) - 2
Dim lbl As New Label
lbl.AutoSize = False
lbl.Width = intWidth
lbl.Height = intHeight
lbl.TextAlign = ContentAlignment.MiddleCenter
lbl.BorderStyle = BorderStyle.FixedSingle
lbl.Tag = ActiveState.InActive
Return lbl
End Function
The preceding Function creates a Label control object and sets its settings. You will create a label for each cell in the gaming board, which you will create now.
C#
private void frmBingo_Shown(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
lblCurrent.TextAlign = ContentAlignment.MiddleRight;
tblBingo.Controls.Clear();
tblBingo.ColumnStyles.Clear();
tblBingo.RowStyles.Clear();
if (tblBingo.Width < intMinWidth)
tblBingo.Width = intMinWidth;
if (tblBingo.Height < intMinHeight)
tblBingo.Height = intMinHeight;
float sngColumns = System.Convert.ToSingle
(100 / (double)chrHeader.Length);
float sngRows = System.Convert.ToSingle
(100 / (double)(intRows + 1));
tblBingo.ColumnCount = chrHeader.Length;
tblBingo.RowCount = intRows + 1;
for (int idx = 0; idx <= chrHeader.Length - 1; idx++)
tblBingo.ColumnStyles.Add(new ColumnStyle(SizeType
.Percent, sngColumns));
for (int idx = 0; idx <= intRows; idx++)
tblBingo.RowStyles.Add(new RowStyle(SizeType
.Percent, sngRows));
for (int iCol = 0; iCol <= chrHeader.Length - 1;
iCol++)
{
Label lbl = lblLabel();
lbl.Text = chrHeader[iCol].ToString();
tblBingo.Controls.Add(lbl, iCol, 0);
for (int iRow = 1; iRow <= intRows; iRow++)
{
lbl = lblLabel();
lbl.Click += lblClick;
lbl.Text = chrHeader[iCol].ToString() + ' ' +
(iCol * intRows + iRow).ToString();
tblBingo.Controls.Add(lbl, iCol, iRow);
dicCards.Add(lbl.Text, lbl);
}
}
btnReset.PerformClick();
}
}
}
VB.NET
Private Sub frmBingo_Shown(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Me.Shown
lblCurrent.TextAlign = ContentAlignment.MiddleRight
tblBingo.Controls.Clear()
tblBingo.ColumnStyles.Clear()
tblBingo.RowStyles.Clear()
If tblBingo.Width < intMinWidth Then tblBingo.Width = _
intMinWidth
If tblBingo.Height < intMinHeight Then tblBingo.Height = _
intMinHeight
Dim sngColumns As Single = CSng(100 / chrHeader.Length)
Dim sngRows As Single = CSng(100 / (intRows + 1))
tblBingo.ColumnCount = chrHeader.Length
tblBingo.RowCount = intRows + 1
For idx As Integer = 0 To chrHeader.Length - 1
tblBingo.ColumnStyles.Add(New ColumnStyle(SizeType _
.Percent, sngColumns))
Next
For idx As Integer = 0 To intRows
tblBingo.RowStyles.Add(New RowStyle(SizeType.Percent, _
sngRows))
Next
For iCol As Integer = 0 To chrHeader.Length - 1
Dim lbl As Label = lblLabel()
lbl.Text = chrHeader(iCol)
tblBingo.Controls.Add(lbl, iCol, 0)
For iRow As Integer = 1 To intRows
lbl = lblLabel()
AddHandler lbl.Click, AddressOf lblClick
lbl.Text = chrHeader(iCol) & " " & _
(iCol * intRows + iRow).ToString
tblBingo.Controls.Add(lbl, iCol, iRow)
dicCards.Add(lbl.Text, lbl)
Next
Next
btnReset.PerformClick()
End Sub
You determine the height and width each Bingo cell should be, and then add a label into it. Altogether, you will add 90 cells. You then add an event handler for each label object. You will add this event handler now.
C#
private void lblClick(System.Object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Populate(sender);
}
VB.NET
Private Sub lblClick(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs)
Populate(sender)
End Sub
Add the Populate sub procedure.
C#
private void Populate(System.Object sender)
{
Label lbl = (Label)sender;
if ((ActiveState)lbl.Tag == ActiveState.InActive)
{
intCalledNumbers += 1;
lbl.Tag = ActiveState.Active;
lbl.BackColor = Color.FromArgb((int)ActiveState.Active);
lblCurrent.Text = lbl.Text;
lblAllPicks.Text = lblAllPicks.Text.Insert(0, " . " +
lbl.Text);
if (lblAllPicks.Text.Length > 60)
{
int iIndex = lblAllPicks.Text.LastIndexOf(" ");
lblAllPicks.Text = lblAllPicks.Text.Substring(0,
iIndex);
}
System.Drawing.Point dp = lbl.Location;
dp.X += tblBingo.Location.X + 4;
dp.Y += tblBingo.Location.Y + 4;
Cursor.Position = PointToScreen(dp);
}
}
VB.NET
Private Sub Populate(sender As System.Object)
Dim lbl As Label = CType(sender, Label)
If DirectCast(lbl.Tag, ActiveState) = ActiveState.InActive _
Then
intCalledNumbers += 1
lbl.Tag = ActiveState.Active
lbl.BackColor = Color.FromArgb(ActiveState.Active)
lblCurrent.Text = lbl.Text
lblAllPicks.Text = lblAllPicks.Text.Insert(0, " . " _
& lbl.Text)
If lblAllPicks.Text.Length > 60 Then
Dim iIndex As Integer = _
lblAllPicks.Text.LastIndexOf(" ")
lblAllPicks.Text = lblAllPicks.Text.Substring(0, _
iIndex)
End If
Dim dp As Drawing.Point = lbl.Location
dp.X += tblBingo.Location.X + 4
dp.Y += tblBingo.Location.Y + 4
Cursor.Position = PointToScreen(dp)
End If
End Sub
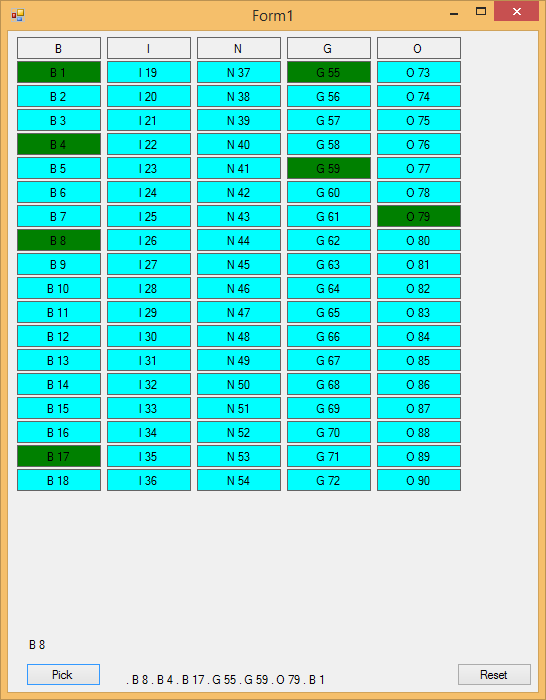
The Populate sub procedure fills in the cells, depending on their respective states. It also adds a dot next to the called number. If you were to run your project now, you might see a screen similar to Figure 2.
Figure 2: Game board
Add the code for the Pick and Reset buttons.
C#
private void btnPick_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (intCalledNumbers >= intTotalCells)
{
lblCurrent.Text = "Game over";
return;
}
List<KeyValuePair<string, Label>> lstNotCalled;
lstNotCalled = (from kvp in dicCards
where (ActiveState)kvp.Value.Tag ==
ActiveState.InActive
select kvp).ToList();
if (lstNotCalled.Count > 0)
{
int idx = rndRand.Next(lstNotCalled.Count);
KeyValuePair<string, Label> foo = lstNotCalled[idx];
Populate(foo.Value);
}
}
private void btnReset_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
foreach (KeyValuePair<string, Label> kvp in dicCards)
{
kvp.Value.BackColor =
Color.FromArgb((int)ActiveState.InActive);
kvp.Value.Tag = ActiveState.InActive;
}
intCalledNumbers = 0;
lblCurrent.Text = "Reset";
lblAllPicks.Text = "";
btnPick.Select();
}
VB.NET
Private Sub btnReset_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnReset.Click
For Each kvp As KeyValuePair(Of String, Label) In dicCards]
kvp.Value.BackColor = Color.FromArgb(ActiveState.InActive)
kvp.Value.Tag = ActiveState.InActive
Next
intCalledNumbers = 0
lblCurrent.Text = "Reset"
lblAllPicks.Text = ""
btnPick.Select()
End Sub
Private Sub btnPick_Click(sender As System.Object, _
e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnPick.Click
If intCalledNumbers >= intTotalCells Then
lblCurrent.Text = "Game over"
Exit Sub
End If
Dim lstNotCalled As List(Of KeyValuePair(Of String, Label))
lstNotCalled = (From kvp In dicCards Where _
DirectCast(kvp.Value.Tag, ActiveState) = _
ActiveState.InActive Select kvp).ToList
If lstNotCalled.Count > 0 Then
Dim idx As Integer = rndRand.Next(lstNotCalled.Count)
Dim foo As KeyValuePair(Of String, Label) = _
lstNotCalled(idx)
Populate(foo.Value)
End If
End Sub
A Random number gets picked and filled with Green inside the Pick button; Reset resets everything back to their default values. Instantiate the necessary objects inside the C# program’s constructor.
C#
public frmBingo()
{
InitializeComponent();
intTotalCells = intRows * chrHeader.Length; ;
}
In Visual Basic, this step is not needed.
Your running program will look like Figure 3.
Figure 3: Running
Conclusion
Well, there you have it! Bingo is not too difficult to do, as with any other game. All you need is a bit of logic and time.